Understanding Why Zero Factorial Equals One: A Deep Dive
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Factorials
The concept of zero factorial equaling one is widely accepted, taught in middle school mathematics. However, many of us may not fully grasp why this is the case. It’s common in math to accept statements at face value, often out of fear of appearing uninformed by questioning them. When a teacher states that 0! = 1, we might feel compelled to accept it without further inquiry. But why not challenge that assertion? Understanding the reasoning behind it is crucial for our mathematical literacy.
In this exploration, I aim to clarify why 0! equals 1 through straightforward, incremental puzzles that everyone can follow. If you’ve read my previous article explaining why any number to the power of zero equals one, you’ll find that we will utilize a similar approach here.
Section 1.1: What is a Factorial?
A factorial is a mathematical function applied to non-negative integers. When we apply this function to an integer n, it produces a multiplicative series of all positive integers up to n. Let’s look at some examples for clarity:
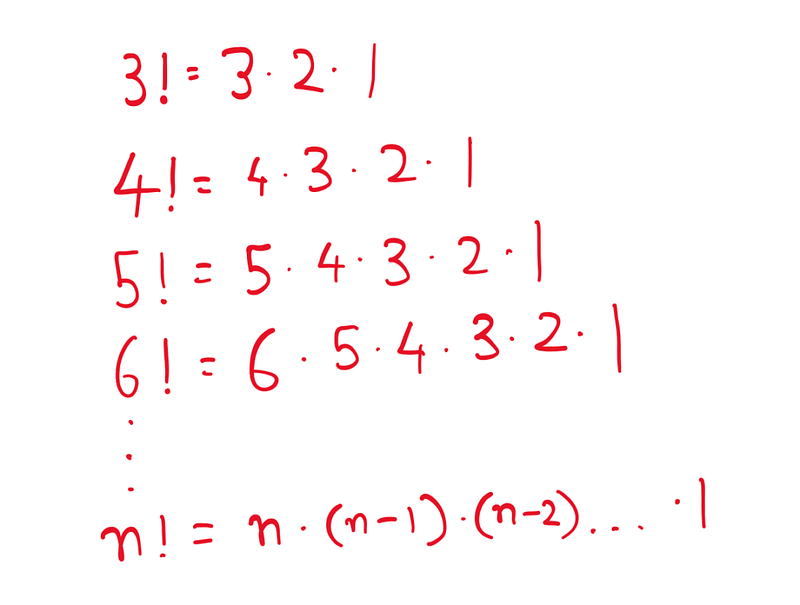
The essential takeaway is that the process involves multiplying integers in descending order until reaching 1. This pattern holds true for any positive integer. However, when it comes to zero, things become less clear. What happens when we calculate the factorial of zero? While it may not seem straightforward at first, I assure you it isn’t as complicated as it appears. We’ll examine how the factorial function behaves as we navigate through the integers.
Subsection 1.1.1: Factorials Ascending
Let’s start with the factorial of 1: 1! = 1, since there are no positive integers smaller than 1. If we want to calculate 2!, we simply multiply by 2, leading to 2! = 2 * 1. Following this pattern, we can compute 3! by multiplying 2! by 3. Here are some worked examples for better understanding:
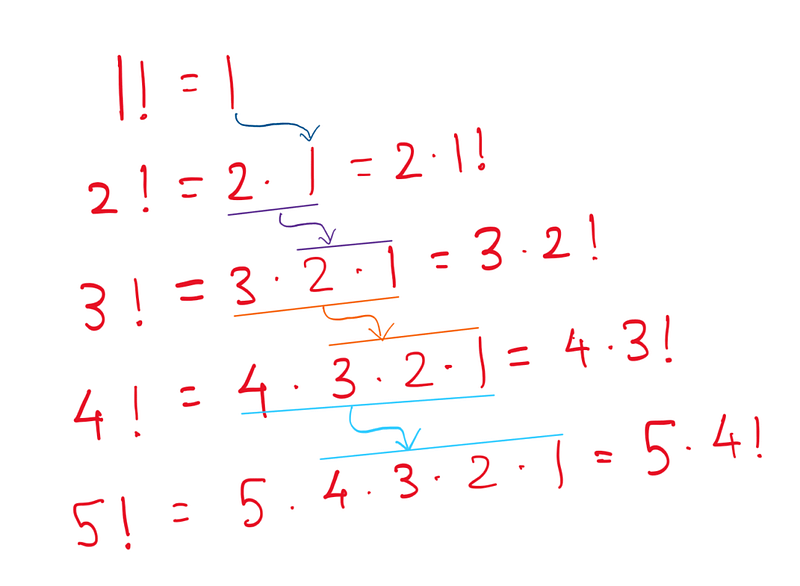
From these examples, we see that the factorial of any integer n is the product of n and the factorial of (n-1). For instance, 4! = 4 * 3!, and 5! = 5 * 4!. This observation will prove useful as we continue.
Section 1.2: Factorials Descending
Now, let’s reverse our approach. Starting from 5!, how do we arrive at 4!? To decrease by one integer, we divide by 5. Likewise, to go from 4! to 3!, we divide by 4. Here are the corresponding examples:
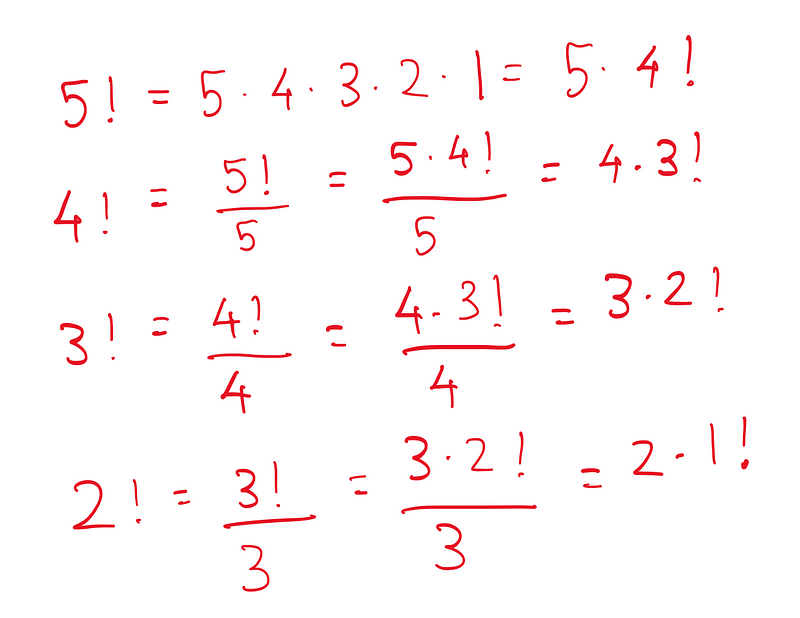
The critical point to remember is that to reduce n! to (n-1)!, we divide n! by n, or n!/n.
Chapter 2: Arriving at Zero Factorial
Now that we’ve navigated the factorial function through the integers, let’s continue down to zero. What happens as we calculate 2! down to 1!, and so forth?
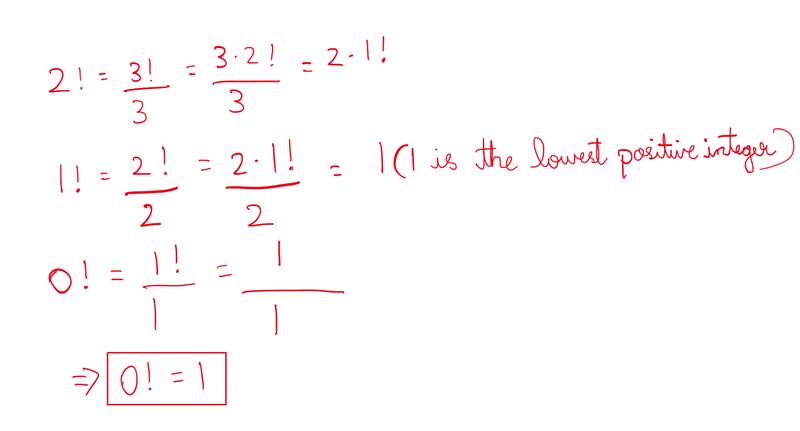
As we descend to zero, we uncover that 0! equals 1 because it represents 1! divided by 1 (1!/1). This conclusion aligns with our understanding of the factorial function, removing the need for blind acceptance of mathematical facts.
I hope you found this exploration enlightening and beneficial. If you appreciate my work, consider showing your support by clapping, following, or subscribing.
Further reading that may interest you: Why is 3 A Special Denominator In Division? and How To Use Mathematics To Choose A Life Partner?
You can read the original essay here.
In this video, "Zero Factorial - Numberphile," you'll discover more about the fascinating topic of zero factorial and its implications in mathematics.
The video "Prove that Zero Factorial is Equal to One" delves deeper into the mathematical proof behind this intriguing concept.