The Marvelous Heart: Exploring Its Endless Resilience and Future
Written on
Chapter 1: The Heart's Unwavering Drive
Have you ever wondered why our hearts never seem to tire? This vital organ, which beats non-stop throughout our lives, is a complex and beautifully designed pumping system. Understanding how it operates can deepen our appreciation for its role in our health.
The heart is an extraordinary organ that pulsates around 100,000 times each day, continuously delivering oxygen and nutrients to our bodies. Unlike other muscles, it possesses unique characteristics and structures that prevent fatigue.
Understanding the Marvel of Cardiac Endurance
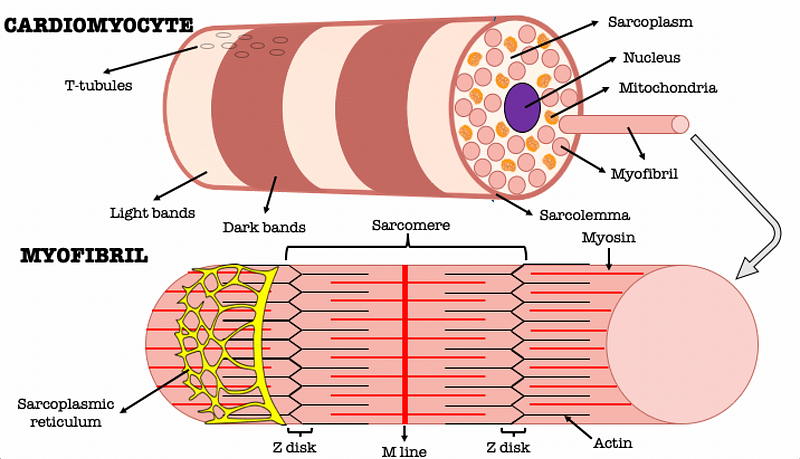
At the heart of this endurance is the cardiac muscle, primarily composed of specialized cells known as cardiomyocytes.

These cells are incredibly resistant to fatigue, largely due to their high mitochondrial density. Mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of cells, produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is essential for energy transfer. In fact, cardiac muscle has up to ten times more mitochondria than skeletal muscle, ensuring a robust energy supply.
Enhanced Blood Supply
Moreover, cardiomyocytes receive a superior blood supply, allowing them to extract oxygen from the bloodstream more effectively than typical muscle cells.
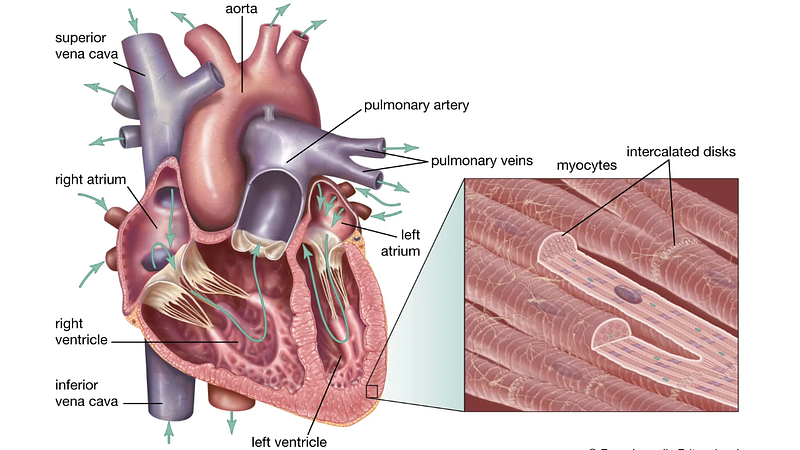
This efficient oxygen and nutrient delivery system is crucial for the heart's continuous operation and overall endurance.
Fuel Flexibility: An Adaptive Mechanism
The heart also demonstrates remarkable adaptability in fuel consumption. Unlike other muscles that rely on a singular energy source, the heart can utilize various fuels, such as glucose, free fatty acids, and lactate. This versatility allows it to maintain function even when specific energy sources are limited.
Non-stop Contraction
A defining trait of the heart is its ability to contract continuously, unlike skeletal muscles, which are attached to bones and have limited endurance.
The systole phase marks the contraction of the heart muscle, propelling blood into the arteries. The first number in a blood pressure reading, known as systolic blood pressure, reflects the force exerted during this contraction. Cardiac muscle is uniquely suited for perpetual contraction and relaxation, facilitating its rhythmic beating essential for life.
In summary, the heart's endurance is a product of its specialized structure, which includes resilient cardiomyocytes, a rich blood supply, and flexible energy utilization. These attributes empower the heart to operate continuously, playing a vital role in sustaining life.
Understanding the Heart's Function
The heart's primary purpose is to pump blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. Its intricate functioning involves a sophisticated electrical system, regulation of blood flow, and rhythmic contractions.
Electrical System
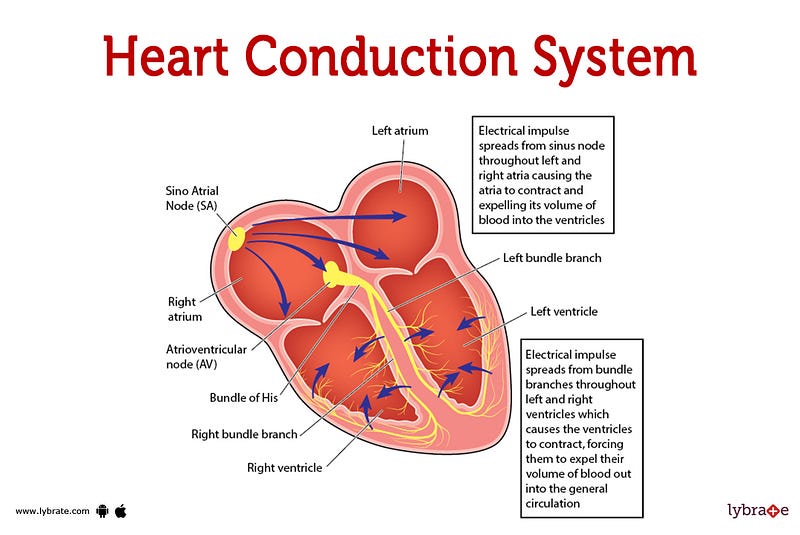
The heart's pumping action is carefully controlled by an electrical conduction system that coordinates the contraction of its various chambers.
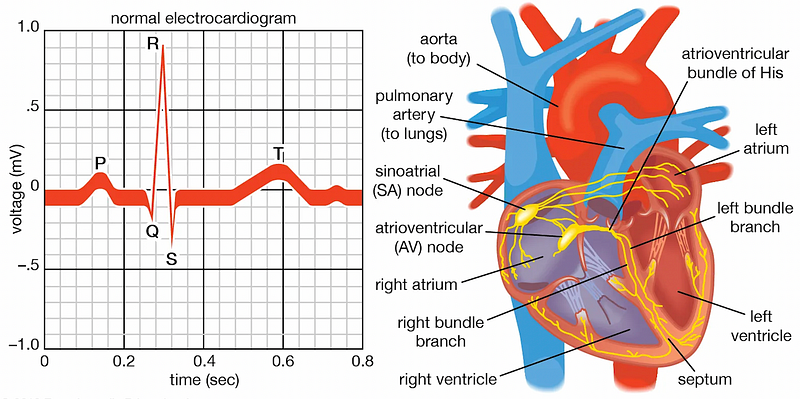
The electrical impulse begins at the sinoatrial (SA) node in the right atrium, traveling through the atrioventricular (AV) node and down to the ventricles via the bundle of His. This coordinated system ensures synchronized and effective pumping.
Blood Flow Coordination
Integral to the heart's function is its capability to pump blood efficiently. The heart’s pumping action is intricately linked to its electrical conduction system, ensuring a rhythmic and effective process.
Rhythmic Contractions
At the heart of the organ's function lies its rhythmic contraction and relaxation, powered by its electrical system. This synchronized action propels blood throughout the circulatory system, providing essential nutrients and oxygen.
Caring for Your Heart: A Vital Responsibility
The significance of physical activity for heart health cannot be overstated. Regular exercise plays a crucial role in promoting cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Risk Reduction
Engaging in physical activity significantly lowers the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Exercise improves blood flow, reduces blood pressure, and raises HDL cholesterol levels, collectively enhancing cardiovascular health.
Cardiovascular Improvement
Routine physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, helps maintain a healthy weight, and alleviates stress. A lower resting heart rate is typically associated with better heart function, as seen in trained athletes who may have rates as low as 40 beats per minute.
Mental Well-being
Exercise not only benefits physical health but also positively impacts mental health, reducing stress and lowering the risk of depression—factors that are crucial for heart health.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for heart health. Regular exercise combined with a balanced diet helps achieve and sustain optimal weight, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease.
Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity
Exercise also enhances glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, which are vital for preventing type 2 diabetes, a condition closely tied to heart health.
Chronic Inflammation Reduction
Regular physical activity helps lower chronic inflammation, a contributing factor to heart disease. The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise bolster cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, exercise is a multifaceted approach to promoting heart health, positively influencing physical fitness, mental well-being, weight management, and reducing chronic inflammation.
Top 5 Ways to Improve Heart Health
- Manage Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease. Lifestyle adjustments, including regular exercise and a healthy diet, are essential for managing blood pressure.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight significantly increases heart disease risk. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through exercise and a balanced diet is crucial.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise five days a week is vital for heart health.
- Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet: A diverse diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports cardiovascular health.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Quitting can lower blood pressure and heart rate, reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
In summary, these five strategies—blood pressure management, maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, heart-healthy eating, and quitting smoking—provide a comprehensive approach to improving heart health.
3D-Printed Hearts: A Glimpse into the Future
Recent advances in medical technology have opened new possibilities for organ transplantation, including the potential for 3D-printed hearts.
Current State of 3D-Printed Hearts
Researchers have made significant progress in 3D-printing heart models using various techniques and materials, including human tissues and vessels. These models are invaluable for surgical simulations and education, helping medical professionals improve their skills and understanding of cardiac conditions.
Challenges in 3D-Printed Heart Transplants
However, creating fully functional human hearts for transplantation remains a significant challenge. While advancements have been made in printing heart models, achieving the complexity required for a functional organ is still a formidable task.
Future Implications
The potential of 3D printing in organ transplantation is vast. If perfected, this technology could address organ shortages and compatibility issues, allowing for personalized organs tailored to individual patients.
Current Limitations and Ongoing Research
Despite progress, there remains a considerable gap between 3D-printing heart models and producing fully functional organs for transplantation. Ongoing research aims to refine printing techniques, select appropriate materials, and address the intricate vascularization necessary for functional organs.
In conclusion, while strides have been made in 3D printing hearts for educational and research purposes, the journey toward 3D-printed heart transplants is still in progress, requiring significant advancements.
Embracing the Marvel of the Heart
The heart, with its tireless endurance and complex functionality, continues to amaze. Understanding its resilience, caring for it through healthy lifestyle choices, and embracing innovative technologies like 3D printing herald a future where the wonders of the heart captivate us even more.