Improving Query Concurrency in BigQuery: Google's Latest Feature
Written on
Introduction to Query Queues
Last year, Google introduced Query Queues for its SaaS Data Warehouse solution, BigQuery. This feature is now widely available, having transitioned from its preview phase to full deployment. While not entirely new, its introduction is crucial for productive environments, as organizations are hesitant to implement features that may not remain stable.
BigQuery's Query Queue Functionality
With the implementation of Query Queues, BigQuery can now assess query concurrency based on the available slots rather than adhering to a fixed maximum. When the upper limit of concurrent queries is reached, any additional queries will be placed in a queue until processing capacity becomes available.
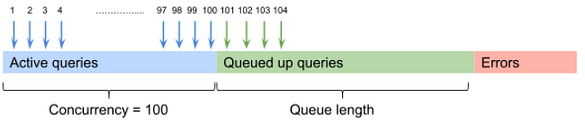
Concurrency plays a vital role in the efficiency of a Data Warehouse, especially when multiple users are accessing the system at the same time. While managing a small number of users can be straightforward, scaling to accommodate thousands presents significant challenges. It is essential for all users to access real-time data without adversely affecting one another or encountering quota errors.
To address these concerns, Google has made Query Queues available by default over the past few weeks, requiring no action from users. Google guarantees that query performance will not suffer as a result of this new feature. Additionally, users have the option to set a maximum concurrency target for their reservations and can manage both interactive and batch query queue timeouts using default settings.
Leveraging Google BigQuery for Data Management
Sources and Additional Information
[1] Google, BigQuery release notes (2023)
[2] Google, Use query queues (2022)