Sickle Cell Disease: A New Era in Gene Therapy Treatment Options
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic disorder that alters the shape of red blood cells, affecting their ability to carry oxygen efficiently throughout the body. Recently, the FDA has approved two innovative treatments aimed at addressing this condition: Casgevy, utilizing CRISPR gene editing, and Lyfgenia, a gene therapy.
As a medical student, I vividly recall a young woman suffering from sickle cell anemia. Though her name escapes me, her strength and resilience during her frequent visits to the emergency room have left a lasting impression on me.
“It will be fine after the thunderstorm. The sun will shine, and it will be nice and warm.” — Mouloud Benzadi
New Advances in Gene Therapy for Sickle Cell
The emergence of these novel gene therapies marks a significant advancement in the treatment landscape for sickle cell disease, potentially offering a "functional cure" for many patients.

In this section, we will delve into the advantages and challenges posed by these gene editing techniques in managing sickle cell disease.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
Sickle cell disease is characterized by a mutation that transforms normally round and flexible red blood cells into rigid, crescent-shaped cells. This alteration can lead to severe complications, including blood clots and pain episodes.
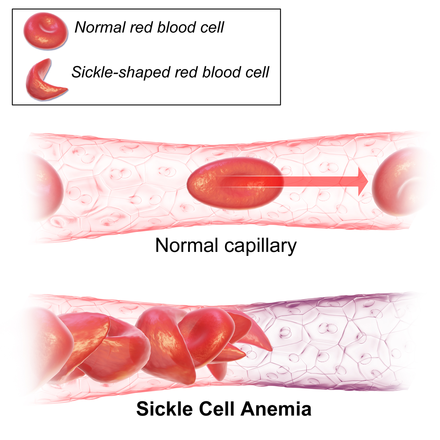
According to the U.S. CDC, sickle cell disease affects approximately 1 in 365 Black babies born in the U.S., with about 100,000 individuals diagnosed with the condition, predominantly among those of African descent.
Who is Affected by Sickle Cell Disease?
Sickle cell disease is inherited, requiring an individual to receive two faulty genes—one from each parent—to develop the disorder. Carriers, who have only one copy of the gene, are generally healthy but can have affected offspring if they partner with another carrier.
Clinical Implications and Management
Patients with sickle cell disease often endure painful "crises" due to blood vessel blockages caused by the abnormal red blood cells. The severity of the disease varies, necessitating ongoing medical support.
Dr. Nicole Verdun from the FDA emphasizes the critical need for effective treatments, noting that sickle cell disease is a severe, life-threatening condition.
FDA's Approval of Gene-Editing Therapies
The recent FDA approvals for Casgevy and Lyfgenia represent substantial progress, yet there are challenges ahead. Patients will need to undergo preparations, including chemotherapy, and may face a prolonged hospital stay.
Despite potential fertility concerns, the medical community is optimistic about these advances.
Gene editing could be a game changer for patients with sickle cell disease - This video discusses the transformative potential of gene editing in treating sickle cell disease and the implications for patient care.
The Significance of Approval
Historically, treatment options for sickle cell disease have been limited. President Biden has praised the FDA's approval as a pivotal moment in medical innovation, offering hope to millions with rare diseases.

Notably, symptoms of sickle cell disease can include intense pain, fatigue, and complications like strokes, with an average life expectancy around 53 years.
Understanding Functional Cures
While these new treatments are not definitive cures, they are referred to as "functional cures," meaning patients can live without showing symptoms of the disease. The collaboration between Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics has led to the first FDA-approved CRISPR therapy.
This innovative approach does not correct the specific genetic defect but instead prompts the body to produce healthy red blood cells. Casgevy enables the body to revert to producing a fetal form of hemoglobin, while CRISPR modifies stem cells from the patient.
Lyfgenia: A Different Approach
Lyfgenia, developed by BlueBird Bio, represents another FDA-approved treatment for individuals aged 12 and above. This therapy employs a viral method to introduce new genetic material, aiming to alleviate pain crises.
Both therapies have demonstrated remarkable success in clinical trials, significantly reducing pain episodes and reliance on blood transfusions.
Potential Risks and Considerations
However, the FDA has cautioned about possible "off-target" effects, which could result in unintended consequences. Lyfgenia carries a serious warning regarding the potential risk of developing leukemia.

Final Thoughts: A New Horizon in Sickle Cell Treatment
The approval of these treatments signifies a hopeful future for individuals with sickle cell disease, honoring the bravery of clinical trial participants who have contributed to this medical advancement.
Many trial participants report life-changing results, highlighting the treatments' potential to transform lives.
The Price of Progress
However, the high cost of these therapies—$2.2 million for Casgevy and $3.1 million for Lyfgenia—raises concerns about accessibility. Dr. Peter Marks estimates that approximately 20,000 patients could benefit from these treatments, though many affected individuals reside in regions where such options remain out of reach.
I remain cautiously optimistic that the young woman I met during my medical training is among those who might benefit from these groundbreaking advancements.
Could gene therapy be a gamechanger in the fight against sickle-cell anemia? | DW News - This video explores the potential of gene therapy in revolutionizing treatment strategies for sickle cell anemia.