The Quantum Computing Race: Insights and Innovations
Written on
Quantum computers have the potential to drive significant advancements across various fields, including scientific research, healthcare, machine learning, materials science, financial planning, and resource allocation algorithms for emergency services.
But what exactly is quantum computing, and what is required to unlock its potential? This article will provide a concise overview of quantum computers and the recent developments within this exciting domain. The discussion is organized into two main sections:
- Fundamentals of Quantum Computing
- Recent Advances and Competitive Landscape
Basics of Quantum Computing
Why Opt for Quantum Computing?
Certain complex problems exceed the capabilities of classical computers, which cannot deliver solutions with current technology. Quantum computers are designed to tackle specific computational challenges—such as integer factorization, which is crucial for RSA encryption—significantly faster than traditional computers. These quantum systems hold the promise of surpassing even the most advanced supercomputers available today.
Understanding the Quantum Computer's Unique Features
As highlighted previously, quantum computers differ from both classical machines and supercomputers. The core of this technology lies in quantum bits or qubits. These qubits, often subatomic particles like electrons or photons, can be manipulated in various ways. Notably, companies such as IBM, Google, and Rigetti Computing utilize superconducting circuits that are cooled to temperatures below that of deep space. Others, like IonQ, employ electromagnetic fields to trap individual atoms on silicon chips within ultra-high vacuum environments. The aim is to maintain the qubits in a stable quantum state.
Qubits exhibit unique quantum characteristics that allow them to perform exponentially more computations than classical bits. Two essential properties are:
- Superposition: Qubits can exist in multiple states (0 and 1) simultaneously, enabling parallel processing.
- Entanglement: Pairs of qubits can become entangled, meaning the state of one qubit can instantaneously affect the state of another, regardless of distance.
Qubits are subject to decoherence, which is a challenge in quantum computing. This phenomenon occurs when qubits interact with their surroundings, causing their quantum states to deteriorate.
What Does Quantum Supremacy Mean?
Quantum supremacy refers to the milestone when a quantum computer can execute a calculation that is impossible for the most powerful classical computers. Coined by John Preskill in 2012, the precise number of qubits needed to achieve this remains uncertain as researchers continuously develop new algorithms that improve classical computing performance. The term quantum advantage is now also widely used, though it lacks the impact of “supremacy.”
Many in the research community debate the significance of this achievement. Rather than wait for a definitive declaration of supremacy, various companies, including IBM, Rigetti, and D-Wave, as well as Chinese firms like Alibaba, are actively experimenting with quantum computers.
The potential for quantum supremacy includes the ability to perform previously unimaginable tasks. For further insight, watch the video by renowned quantum physicist and Professor Shohini Ghose.
Quantum Computer Developments
Various quantum computing models are identified by their unique computational elements. The four principal models of interest include:
- Quantum gate array
- One-way quantum computer
- Adiabatic quantum computer
- Topological quantum computer
Different physical implementations of quantum computers are also being explored, such as:
- Superconducting quantum computing
- Trapped ion quantum computer
- Neutral atoms in optical lattices
- Quantum dot computers, spin-based
- Quantum dot computers, spatial-based
To learn more about quantum computers, watch the following video:
For those interested in programming quantum computers, consider reading Dr. James Wootton's article on creating Battleships from quantum NOT gates.
Quantum Pioneers
Numerous companies, including IBM, Alibaba, Intel, Google, Microsoft, D-Wave Systems, IonQ, and Honeywell, are actively advancing the field of quantum computing. Many collaborate with prominent academic research teams to achieve notable progress, with each vying for the title of the most efficient quantum computer. Below is a brief overview of their achievements and competition:
- IBM: Launched the IBM Q Experience, making a 5-qubit quantum computer publicly accessible online. Over time, they introduced a 20-qubit and then a 50-qubit machine, culminating in the announcement of the IBM Q System One as the "world’s first integrated universal approximate quantum computing system."
- Google: Announced its 72-qubit quantum processor, Bristlecone, in 2018. By 2019, they claimed to have achieved quantum supremacy with their Sycamore processor, which could perform a complex task in 200 seconds that would take a classical supercomputer approximately 10,000 years.
- Alibaba: Collaborated with the Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2015 to establish the CAS–Alibaba Quantum Computing Laboratory, launching a superconducting quantum computing cloud in 2018.
- Microsoft: Announced the delivery of a 49-qubit test processor called Tangle Lake in early 2018, with plans to transition to production-level quantum computing by 2025.
- D-Wave Systems: Sold the D-Wave One, a 128-qubit machine, to Lockheed Martin in 2011, followed by larger machines in subsequent years. Despite their achievements, D-Wave's approach has faced criticism for being restrictive.
- IonQ: A leader in trapped-ion quantum computing, claiming its technology offers unrivaled physical performance and scalability.
- Honeywell: Announced in 2020 that it had developed the highest-performing quantum computer to date.
Major Rivalries in Quantum Computing
The technology race between the USA and China is intense, particularly in the realm of quantum computing.
Google (2019) - USA: On October 23, 2019, Google declared that it had achieved quantum supremacy, utilizing a 53-qubit processor named Sycamore. They claimed their processor completed a task in 200 seconds that would take classical supercomputers around 10,000 years. However, IBM challenged this claim, asserting that the computation could be performed on a classical computer in just 2.5 days.
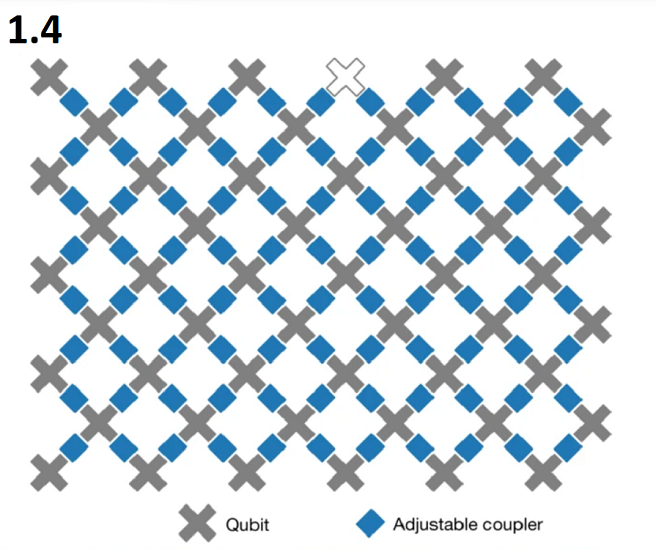
USTC (2020) - China: In December 2020, Chinese researchers reported that their photonic quantum computer, named Jiuzhang, completed a calculation impossible for conventional computers. This system demonstrated the potential to outperform the fastest supercomputers by a significant margin.
While the journey to achieving quantum supremacy is complex and challenging, many companies are committed to developing efficient quantum computers. The promise of quantum computing lies in its potential to dramatically reduce time complexity for quantum algorithms. Currently, no verified evidence of supremacy has been established.
If you're interested, several organizations, including IBM and Google, offer free access to quantum computing resources. You can experiment with algorithms to contribute to the field's advancement.
For those wanting to take a free quantum computing course, additional resources are available.
Thank you for reading.
I hope you found this exploration of ‘The Quantum Computing Race: Insights and Innovations’ informative. Please share your thoughts or comments with us.
Reference: 1. https://www.technologyreview.com/2019/01/29/66141/what-is-quantum-computing/ 2. https://www.quantamagazine.org/john-preskill-explains-quantum-supremacy-20191002/ 3. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_computing#Quantum_computing_models 4. https://www.ibm.com/quantum-computing/learn/what-is-quantum-computing/ 5. https://www.explainingcomputers.com/quantum.html 6. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-019-03213-z 7. https://www.sciencenews.org/article/new-light-based-quantum-computer-jiuzhang-supremacy 8. https://www.livescience.com/china-quantum-supremacy.html
Contact Me:
Academic Website — aritraroy.netlify.app Developer Website — designeraritra.netlify.app E-mail — [email protected]
Follow Me:
LinkedIn — https://www.linkedin.com/in/aritraroy24/ GitHub — https://github.com/aritraroy24